Cybersecurity - Fighting the Good Fight Infographic
Fighting the Good Fight: An Inside Look at Ethical Hacking and Careers in Cybersecurity
The term “hacker” often has a negative connotation, bringing to mind the image of a hooded criminal behind a computer shrouded in darkness. However, the methods employed by criminal hackers to gain illegal access to private information are also being used by ethical hackers to keep data safe. To learn more, check out the infographic below created by St. Bonaventure University.
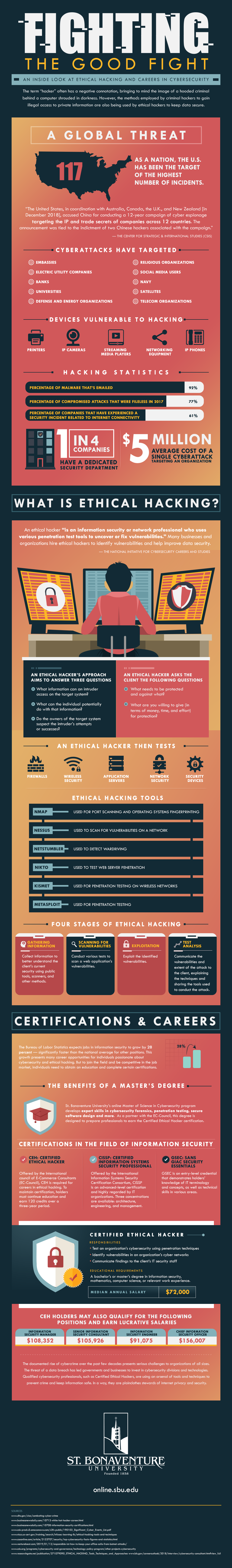
A Global Threat
As a nation, the United States has been the target of 117 cyber-related incidents – the highest number of targets in the world. According to The Center for Strategic & International Studies (CSIS), “The United States, in coordination with Australia, Canada, the U.K., and New Zealand [in December 2018], accused China for conducting a 12-year campaign of cyber espionage targeting the IP and trade secrets of companies across 12 countries. The announcement was tied to the indictment of two Chinese hackers associated with the campaign.” Cyberattacks have targeted a wide range of entities, including embassies, banks, universities, religious organizations, social media users, and telecom organizations. The devices deemed vulnerable to hacking include printers, streaming media players, networking equipment, and IP cameras and phones.
Hacking Statistics
Studies indicate that 92% of malware arrives via e-mail. They also indicated that 77% of the compromised attacks registered in 2017 were file-less, and that 61% of companies have experienced some type of security incident related to internet connectivity. Just one in four companies have a dedicated security department, even though having one in place could make a huge difference. Studies indicate the average cost of a single cyberattack targeting an organization is $5 million.
What is Ethical Hacking?
According to the National Initiative for Cybersecurity Careers and Studies, an ethical hacker “is an information security or network professional who uses various penetration test tools to uncover or fix vulnerabilities.” Many companies and organizations hire ethical hackers to spot vulnerabilities and help improve data security. An ethical hacker’s approach aims to answer three questions. Firstly, they seek to answer what information can an intruder access on a target system. They also look to see what the individual hacker may be able to potentially do with their information. Finally, they determine whether the owners of the target system suspect the intruding hacker’s attempts or successes. An ethical hacker also approaches a system with a couple questions for the client that hires their services. Specifically, they ask to find out what needs to be protected and from what type of interested party. They’ll also ask what kind of money, time, and effort the client is willing to give for protection. Once these questions are answered, the ethical hacker will test numerous systems, including firewalls, wireless security, application servers, network security, and security devices.
Ethical Hacking Tools
An ethical hacker will deploy several tools to detect vulnerabilities. These tools focus on specific aspects of hacking. For instance, they may use NMAP for port scanning and operating systems fingerprinting. They may also deploy Nikto to test web server penetration, or they could use Metasploit for penetration testing.
Four Stages of Ethical Hacking
There are four distinct stages to the ethical hacking process. The first stage is built around gathering information, which is done to better understand the client’s current security using public tools, scanners, and other methods. The next stage involves scanning for vulnerabilities, which is done by conducting various scanning tests. The third stage involves the exploitation of any identified vulnerabilities. The process concludes with test analysis, where the ethical hacker communicates the vulnerabilities and the extent of the attack to the client while also explaining the techniques and tools used to conduct the ethical attack.
Certifications & Careers in Cyber Security
The Bureau of Labor Statistics expects jobs in information security to grow by 28 percent, which is substantially faster than the national average given to other positions. This growth presents many career opportunities for individuals passionate about cybersecurity and ethical hacking. However, to join the field and be competitive in the job market, individuals need to obtains an education and complete certain certifications.
The Benefits of a Master’s Degree in Cyber Security
St. Bonaventure University’s online Master of Science in Cybersecurity program develops expert skills in cybersecurity forensics, penetration testing, secure software design, and more. As a partner with the EC-Council, this degree is designed to prep professionals to earn the Certified Ethical Hacker certification. There are a few information security certifications that can be obtained. The first is the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), which is required for ethical hacking careers. A second certification, the Certified Information Systems Security Professional, is a highly regarded advanced-level certification that features concentrations in architecture, engineering, and management. Another certification is the GSEC, an entry-level credential that demonstrates a person’s knowledge of IT concepts and technical skills. A certified ethical hacker’s responsibilities typically include testing an organization’s cybersecurity via penetration techniques, identifying vulnerabilities in cyber networks, and communicating the findings with a client’s IT security staff. A bachelor’s degree in math, information security, computer science, or relevant work experience is required for the position. The median annual salary for the position is $72,000, yet qualified ethical hackers could qualify for other information security positions that offer more lucrative salaries. The documented rise of cybercrime over the past few decades presents serious challenges to organizations of all sizes. The threat of a data breach has led governments and businesses to invest in cybersecurity divisions and technologies. Qualified cybersecurity profs like Certified Ethical Hackers are using an array of techniques and tools to prevent crime and keep information safe. In a way, they’re plainclothes stewards of internet privacy and security.

